JAVA Notes
基本程式概念
如果一個程式檔案只有一個類別 ( class ) 定義時,類別名稱就是檔案名稱。
public class <Class_name> {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}- 起始方法
- main ( ) 必須宣告為 public(公開)、static(靜態)、void(沒有回傳值)。
- 其形式參數必須為 String 型別的一維陣列。
- 每一行程式敘述都以『;』符號結尾
- 註解
- 單行註解
// ... - 多行註解
/* ... */
- 單行註解
變數
數值是可以變更的。
- 基本資料型態
byte、int、short、long、float、double、char、boolean
- 宣告變數
int number;long number = 數字L;:若沒有加L/l則會認成 int 型態float number = 數字f;:若沒有加F/f則會認成 double 型態 - 變數的命名規則
- 識別字必須以英文字母開頭,大小寫均可。
_或是$開頭也可以。
- Java 的關鍵字 ( 必定是小寫 )
- boolean、char、byte、short、int、long、float、double
- if、else、switch、break、continue、return、case、do、while、for、goto、const
- new、this、super、void、class、extends、import、package、implements、nstanceof、interface
- try、catch、finally、throw、throws
- public、private、protected、default、final、abstract、static
- native、strictfp、synchronized、transient、volatile
常數
在設定初始值後,就不會變更其值。
- 宣告常數java
final int number;
命名原則
| 種類 | 習慣命名原則 | 範例 |
|---|---|---|
| 常數 | 使用英文大寫字母和底線 _ 符號 | MAX_SIZE、MIN_SIZE |
| 變數 | 小駝峰 | size、screenSize、myAccountNumber |
| 類別 (class) | 大駝峰 | LargeRoom、SmallRoom |
| 函式 (method) | 小駝峰 | pressButton、scrollScreen |
基本資料型態範圍及初始值
| 型別 | 占用記憶體 | 值域 |
|---|---|---|
| Byte | 1 byte | - 2^7 ~ 2^7 -1 |
| Short | 2 bytes | - 2^15 ~ 2^15 -1 ( -32768 ~ 32767 ) |
| int | 4 bytes | - 2^31 ~ 2^31 -1 ( -128 ~ 127 ) |
| long | 8 bytes | - 2^63 ~ 2^63 -1 |
| Char | 2 bytes | '\u0000' ~ '\uFFFF' ( 0 ~ 65535 ) |
| boolean | 1 byte | true / false |
| float | 4 bytes | |
| double | 8 bytes |
字串
- 一種字串物件,屬於參考資料型態。
- 多使用在
System.out.println()或println()函式的參數。 - String 類別初始化的預設值為 null。
String = ""和String = null意思不同
javaString a = null; System.out.print(a);會 print 出
null
System.out.println("String");
跳脫字元
| 逸出字元 | 說明 | Unicode 碼 |
|---|---|---|
\b | Backspace 鍵 | \u0008 |
\f | FF,Form feed 換頁符號 | \u000C |
\n | LF,Line feed 換行符號 | \u000A |
\r | CR,Enter 鍵 | \u000D |
\t | Tab 鍵,定位符號 | \u0009 |
\' | 「'」單引號 | \u0027 |
\" | 「"」雙引號 | \u0022 |
\\ | 「\」符號 | \u005C |
基本型別轉換
- char 型別可以視為 int 型別,但所有整數型別皆不能視為 char 型別。
- 不同型別在做數學運算前,compiler 會自動將小的型別改成大的型別。
- int 與 String 的轉換為:
Integer.toString()/Integer.parseInt() - floating-point types 轉成 integral types 小數點後面直接截掉
-0.0 == 0.0istrue。- 強制型別轉換
(float)a/b將 a 強制轉為 float 型態
陣列
一維陣列
- 宣告並配置陣列java
int[] array; array = new int[3];javaint[] array = new int[3]; - 三者皆相同
int array[]int[] arrayint []array - 取得陣列的長度java
array.length - 設定陣列初值java
Int array[] = {10, 20, 30}; - 存取陣列java
array[index]
二維陣列
- 宣告並配置陣列java
int[] array; array = new int[3][5]; // 3 列 5 行javaint[] array = new int[3][5]; - 設定陣列初值java
int array[3][5] = { {11, 12, 13, 14, 15}, {16, 17, 18, 19, 20}, {21, 22, 23, 24, 25} }; - 每列元素個數不同java
int array[][] = { {11, 12, 13}, {14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19}, {20, 21, 22, 23} };javaint array[] = new int[3][]; array[0] = new int[3]; array[1] = new int[6]; array[2] = new int[4];
多維陣列
- 宣告並配置陣列java
int[] array; array = new int[2][3][5]; // 2 x 3 x 5javaint[] array = new int[2][3][5]; - 設定陣列初值java
int array[2][3][5] = { { {11, 12, 13, 14, 15}, {16, 17, 18, 19, 20}, {21, 22, 23, 24, 25} }, { {31, 32, 33, 34, 35}, {36, 37, 38, 39, 30}, {41, 42, 43, 44, 45} } };
運算子
算術運算子
| 符號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
+ | 加法 |
- | 減法 |
* | 乘法 |
/ | 除法 |
% | 取餘數 |
二元運算子
| 符號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
~ | NOT |
& | AND |
| | OR |
^ | XOR |
邏輯運算子
| 符號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
! | 邏輯 NOT |
&& | 邏輯 AND |
|| | 邏輯 OR |
比較運算子
| 符號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
> | 大於 |
>= | 大於等於 |
< | 小於 |
<= | 小於等於 |
== | 等於 |
!= | 不等於 |
位移運算子
| 符號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
>> | 右移 |
<< | 左移 |
條件運算子
| 符號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
?: | if-else |
連結運算子
| 符號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
{} | 連接變數 |
流程控制
if-else
if (判斷式){
// do something;
} else {
// do something;
}變數 = 判斷式 ? 成立回傳結果 : 不成立回傳結果 ;for loop
for (設定初值 ; 判斷式 ; 設定增減量){
// do something;
}while loop
while (判斷式){
// do something;
}do-while loop
do {
// do something;
} while (判斷式);break 強制脫離迴圈 continue 強制跳過以下程式碼再跑下一圈迴圈
switch
switch (變數) {
case 1:
// do something;
break;
case 2:
// do something;
break;
case 3:
case 4:
// do somethings;
break;
default:
// do something;
}- 記得視需要情況加上
break default可有可無
類別 Class
函式 Function ( method )
public static 型態 函式名稱 ( 參數型態 參數名稱 ){
// do something;
return 回傳值 ( 運算式 );
}修飾子 Modifier
public共有的:外部的 class 都可以存取該資料private私有的:只有 class 內的成員可以存取該資料,以達到保護的作用protected被保護的:同 package 中的 class 可以直接存取,不同 package 中的 class 可以在繼承後的 subclass 直接存取- 沒有添加修飾子:只有同個 package 的成員可以存取該資料
static靜態的:所有的 object 共享,可在沒有建立 object 的情況下直接以 class 呼叫
範例
class Circle {
double pi = 3.14;
double radius;
void printArea() {
System.out.println("area = "" + pi * radius * radius);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main (String args[]){
Circle cir = new Circle();
cir.radius = 5.0;
cir.printArea();
}
}- 將 radius 化成 私有變數
class Circle {
private double pi = 3.14;
private double radius;
void printArea() {
System.out.println("area = " + pi * radius * radius);
}
void setRadius(double r){
radius = r;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main (String args[]){
Circle cir = new Circle();
cir.setRadius(5.0);
cir.printArea();
}
}匯入 package / class
- package:資料夾名稱
- class:通常與檔案名稱相同
import <package>.<class>;- 內置套件 ( In-Build Packages )
這些套件由大量 class 組成,這些 class 是 Java API 的一部分。
java.lang:包含語言支持類別,此套件將自動導入。java.io:包含用於支持輸入 / 輸出操作的類別。java.util:包含實現鏈接列表,字典和支持等數據結構的實用程序類別,用於日期 / 時間操作。java.applet:包含用於創建 Applet 的類別。java.awt:包含用於實現圖形用戶界面組件的類別(如按鈕、菜單等)。java.net:包含用於支持網絡操作的類別。
建構子 Costructor
- 沒有定義 constructor 將會定義一個不帶參數的 constructor,而且不會做任何事
- 可以很多個 Constructor,但需要不同的參數
範例:
public class Human{
String name;
int age;
int height;
private Human(){
}
public Human(String str){
this.name = str;
}
public Human(String str, int a, int b){
this.name = str;
this.age = a;
this.height = b;
}
}- 定義 object 就可以透過 constructor 很輕鬆的設定
public class CallHuman{
public static void main (String[] args){
Human h1 = new Human();
Human h2 = new Human("名稱");
Human h3 = new Human("名稱", 數字a, 數字b);
}
}繼承 Inheritance
範例:
class Father{
public int money=100;
public void getMoney(){
System.out.println("金額:" + money);
}
}
public class Son extends Father{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
son.getMoney();
System.out.println("son 金額=" + son.money);
}
}super()假設父類別是帶有參數的 constructor ,而需要在子類別的 constructor 最前面加上super()
覆寫 Override
- 子類別繼承父類別時,改寫父類別原有的方法內容
- 若要覆寫父類別的 function,則名稱、回傳值的資料型態、參數型態及數量都必須相同
範例:
class Animal {
public void run(int units) {
System.out.println("動物移動" + units + "步");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void run(int units){
System.out.println("狗狗跑" + units + "步");
}
}Swing
產生 Swing
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jframe = new JFrame("視窗名稱"); // 產生視窗
jframe.setSize(視窗寬度, 視窗高度); // 設定視窗大小
jframe.setVisible(true); // 顯示視窗
}
}取消自動版面管理
jframe.setLayout(null);產生元件
JLabel label = new JLabel("內容");
JTextField text = new JTextField();
JButton button = new JButton("內容");JLabel 放置圖片
import java.net.URL;
ImageIcon image = new ImageIcon(new URL("圖片網址"));
JLabel imageLabel = new JLabel(image);
int imageWight = image.getIconWidth(); // 可得到圖片的寬高
int imageHeight = image.getIconHeight();JButton 放置 icon
import java.net.URL;
import java.awt.*;
ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(new URL("icon 網址"));
Image newIcon = icon.getImage().getScaledInstance(寬度, 高度, Image.SCALE_SMOOTH);
icon = new ImageIcon(newIcon);
button.setIcon(icon);設定座標
label.setBounds(x, y, width, height);
imageLabel.setBounds(x, y, imageWight, imageHeight);
text.setBounds(x, y, width, height);
button.setBounds(x, y, width, height);將元件加到畫面上
jframe.add(label);
jframe.add(text);
jframe.add(button);事件處理
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class Swing {
private JPanel panel1;
private JButton button1;
public Swing() {
button1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(panel1, "內容");
}
});
}
}JTree
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JTree() | 使用範例模型創建 JTree |
JTree(Object[] value) | 創建一個 JTree,將參數陣列中的每個元素作為此根節點的子節點。 |
JTree(TreeNode root) | 創建一個以指定 TreeNode 為根的 JTree,會顯示根節點。 |
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.tree.DefaultMutableTreeNode;
public class TreeExample {
TreeExample() {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
DefaultMutableTreeNode style = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Style");
DefaultMutableTreeNode color = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("color");
DefaultMutableTreeNode font = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("font");
style.add(color); // 將 color 加為 style 的子節點
style.add(font); // 將 font 加為 style 的子節點
DefaultMutableTreeNode red = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("red");
DefaultMutableTreeNode blue = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("blue");
DefaultMutableTreeNode black = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("black");
DefaultMutableTreeNode green = new DefaultMutableTreeNode("green");
color.add(red); // 將 red 加為 color 的子節點
color.add(blue); // 將 blue 加為 color 的子節點
color.add(black);
color.add(green);
JTree jt = new JTree(style); // 將 style 作為根節點建構 JTree
frame.add(jt);
frame.setSize(200,200);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TreeExample();
}
}範例輸出: 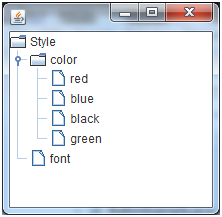
JList 多選選單
JList list = new JList(new String[]{"a", "b", "c"});JScroll 滾輪
JScrollPane scroll = new JScrollPane(list);Combo Box 下拉式選單
可以透過 for 迴圈將內容塞進去
JComboBox combo = new JComboBox();給予內容 ( 選項 )
combo.addItem("內容");combo.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 當選項被選擇時要做的事
}
});JTable
- 只負責呈現資料,本身並不包含任何資料。
- 使用 JTable 必須餵給它資料來源,且必須提供此表格含有幾欄幾列等資訊,也要提供存取資料的方法。
- JTable 用到的資料模型有三種
TableModel ( 表格模型 ) : 負責處理整個表格,主要是針對列
TableColumnModel ( 表格欄模型 ) : 負責處理欄
SelectionModel ( 選取模型 ) : 負責處理資料選取 - 建構子 Constructor
JTable()
JTable(int numRows, int numColumns)
JTable(Object[][] rowData, Object[] columnNames) //固定資料
JTable(TableModel dm)
JTable(TableModel dm, TableColumnModel cm)
JTable(TableModel dm, TableColumnModel cm, ListSelectionModel sm)
JTable(Vector rowData, Vector columnNames) //可變資料概念解析
- JFrame:它是螢幕上視窗的對象,能夠最大化、最小化、關閉。
- JPanel:面板容器,包含在 javax.swing 包中,可以进行嵌套,功能是對視窗中具有相同邏輯功能的組件進行組合,可以加入到 JFrame 視窗中。
- JLabel:可以顯示文字、圖像或同時顯示,在顯示區預設為垂直置中。透過設置垂直和水平對齊方式,指定標籤內容對齊方向:文字標籤是靠左對齊、圖片標籤是水平置中。
- JTextField:可編輯單行文字
JTextField():構造一個新的 TextFieldJTextField(int columns):構造一個具有指定列數的新的空 TextFieldJTextField(String text):構造一個用指定文字初始化的新 TextFieldJTextField(String text, int columns):構造一個用指定文字和列初始化的新 TextField - JPasswordField:允許編輯單行文字,但會用隱藏星號 ( * ) 或點點顯示 ( 密碼形式 )。
- JButton:創建按鈕。
Layout
BorderLayout
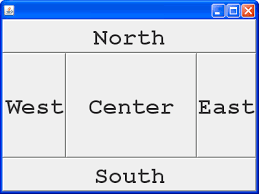
- JFrame、JWindow、JDialog、JInternalFrame 和 JApplet 的內容窗格的默認佈局管理器。
- 元件可放置在容器的四個邊界中或中心。
- 不需要指定容器的所有區域。
- North 與 South 的元件佔據頂部及底部容器的全部寬度,高度是元件的 preferred.height。
- East 和 West 的寬度是元件的 preferred.width,高度是滿足 North 和 South 的高度要求後容器中剩下的部分。
- 剩餘空間都分配給 Center 中的元件。
BorderLayout layout = new BorderLayout();
jframe.setLayout(layout);- 加入元件在指定位置
jframe.add(元件, "North");FlowLayout
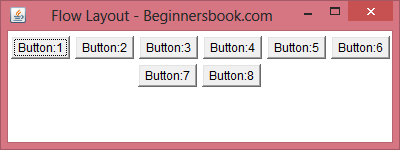
- 配置方式是從左到右,從上到下排列。
- 如果視窗寬度足夠,會將所有的元件放在同一行,否則自動換行。
- 預設元件水平置中對齊,也可以按照需求靠左對齊或者靠右對齊。
- 加入 FlowLayout 版面的元件是按照順序擺放的,所以無法直接指定要擺放的位置。
- 元件放入不會變形,可以加入 JButton 這類元件。
FlowLayout layout = new FlowLayout();
jframe.setLayout(layout);GridLayout

- GridLayout 所切割出來的版面就如同表格版整齊。
- 加入的元件會按照順序從左到右從上到下擺放,所以無法直接指定要擺放的區域。
- 元件放入後會變成方形,所以不適合加入 JButton 這類元件。
- 適合加入 JPanel。
在單行中創建一個 Grid Layout,每個元件默認為一列。
GridLayout layout = new GridLayout();
jframe.setLayout(layout);創建具有指定行數和列數的 Grid Layout。
GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(int rows, int cols);
jframe.setLayout(layout);創建具有指定行數、列數與元件之間水平、垂直間隙的 Grid Layout。
GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(int rows, int cols, int hgap, int vgap);
jframe.setLayout(layout);Servlet
- 記得每個 Servlet 都要繼承 HttpServlet!
- 可在 Servlet 內部
「滑鼠右鍵」→「Insert Code」→「Override Method」勾選需要的 Method
@WebServlet(name = "<servlet_name>", urlPatterns = {"/<網址>"})
public class <servlet_name> extends HttpServlet {
// do somethings
}urlPatterns = {"/<網址>"}:表示這個 Servlet 會掛在此網址上
doGet
範例:
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
try (PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter()) {
/* TODO output your page here. You may use following sample code. */
out.println("<!DOCTYPE html>");
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Servlet HelloServlet</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
out.println("<h1>Servlet WAAAA at " + req.getContextPath() + "</h1>");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
}resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");:宣告型態 ( 給瀏覽器辨識 )
- request:用來讀取瀏覽器過來的資料
HttpServletRequest requestgetParameter()
getParameterNames()
getParameterValues()- response:用來輸出資料到瀏覽器
HttpServletResponse responseaddHeader()
setContentType()
getWriter()傳送資料 via GET
- 在指定網址的時候可以藏參數進去
http://localhost:8080/Test?<key1>=<value1>&<key2>=<value2>
範例:
out.println("<h1> waa" + req.getParameter("name") + "</h1>");輸入網址 http://localhost:8080/Test?name=<value>
傳送資料 via POST
- 傳送大量資料要透過封包
- 前端通常會準備表單
實作 Web Service
| 指令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| GET | 讓 client 取得內容 |
| POST | 讓 client 上傳新內容 |
| PUT | 讓 client 修改既有內容 |
| DELETE | 讓 client 刪除既有內容 |
告知 client 端回傳值為 json
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");將一般的 java 物件直接轉成 json 格式
json 要轉回 java 物件也沒問題
Gson gson = new Gson();
out.println(gson.toJson(user));JSP
JSP Syntax
<% ... %> // 中間編寫 java 語法
<%= ... %> // <% out.println(...); %>
<%@ ... %> // 頁面設定,如 編碼、import...等等內建物件
request:the HttpServletRequestresponse:the HttpServletResponsesession:the HttpSession associated with the requestout:the Writer used to send output to the clientWriter:a buffered vertion of type JspWriter
application:the ServletContext this is a data structure shared by all servlets and JSP pages in the web application and is good for storing shared data